What is a record?
Also known as
Row
Tuple
A record is a group of related data with the same structure. Just like in a traditional spreadsheet, records in a relational database are stored as horizontal rows within a table, and contain values that correspond with that table’s fields, or columns.
Records typically reference a single unit, whether that’s a customer, an order, a session, or some other object that your database captures. A record in a database is usually identified by its value in that table’s entity key field.
Example record
Let’s take a look at the Orders table in Metabase’s Sample Database (figure 1).
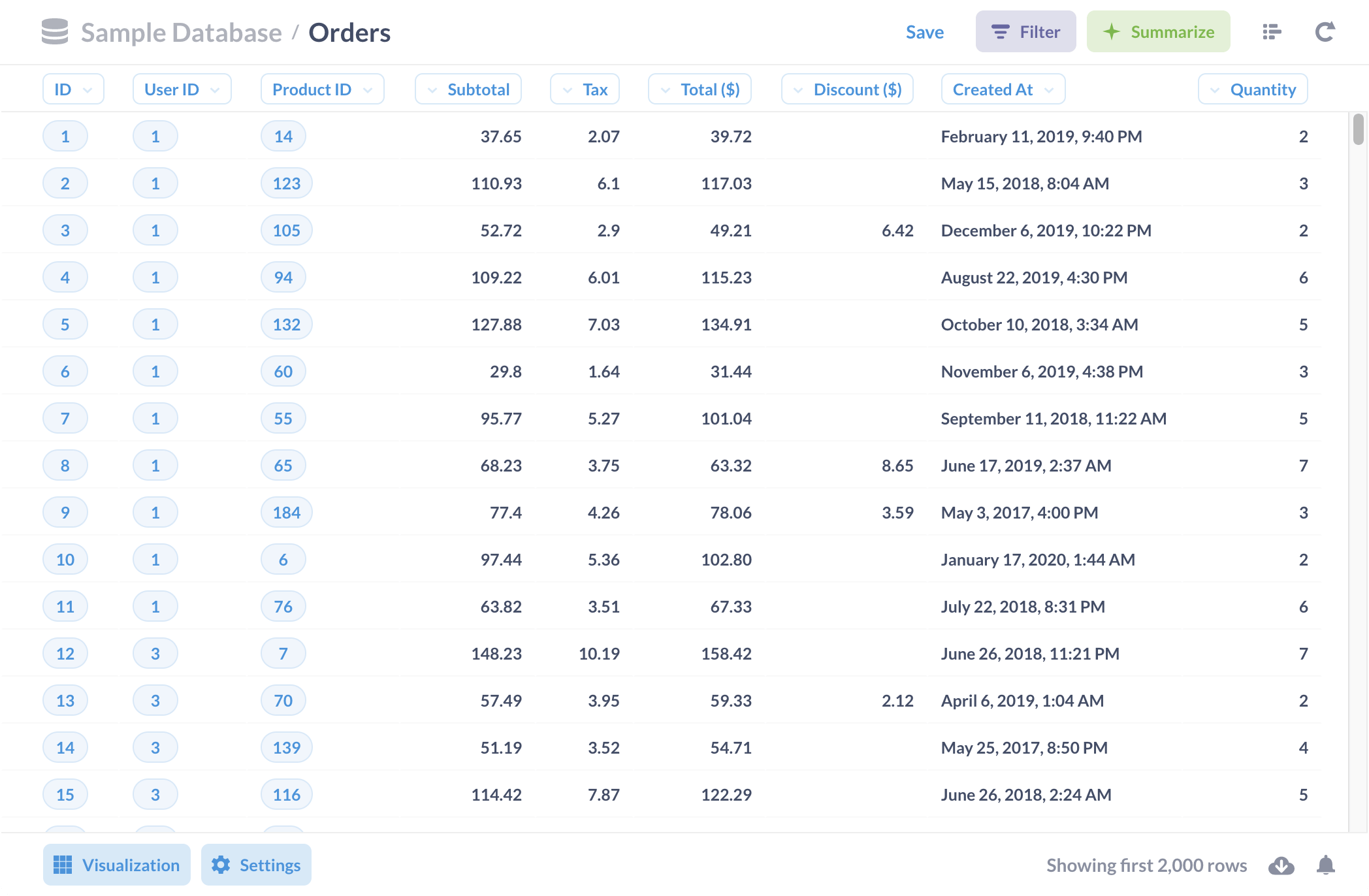
We see the fields in this table (the columns), like ID, User ID, Product ID, Subtotal, and so on. Each record has values that correspond with those fields, and together, those related properties make up one record.
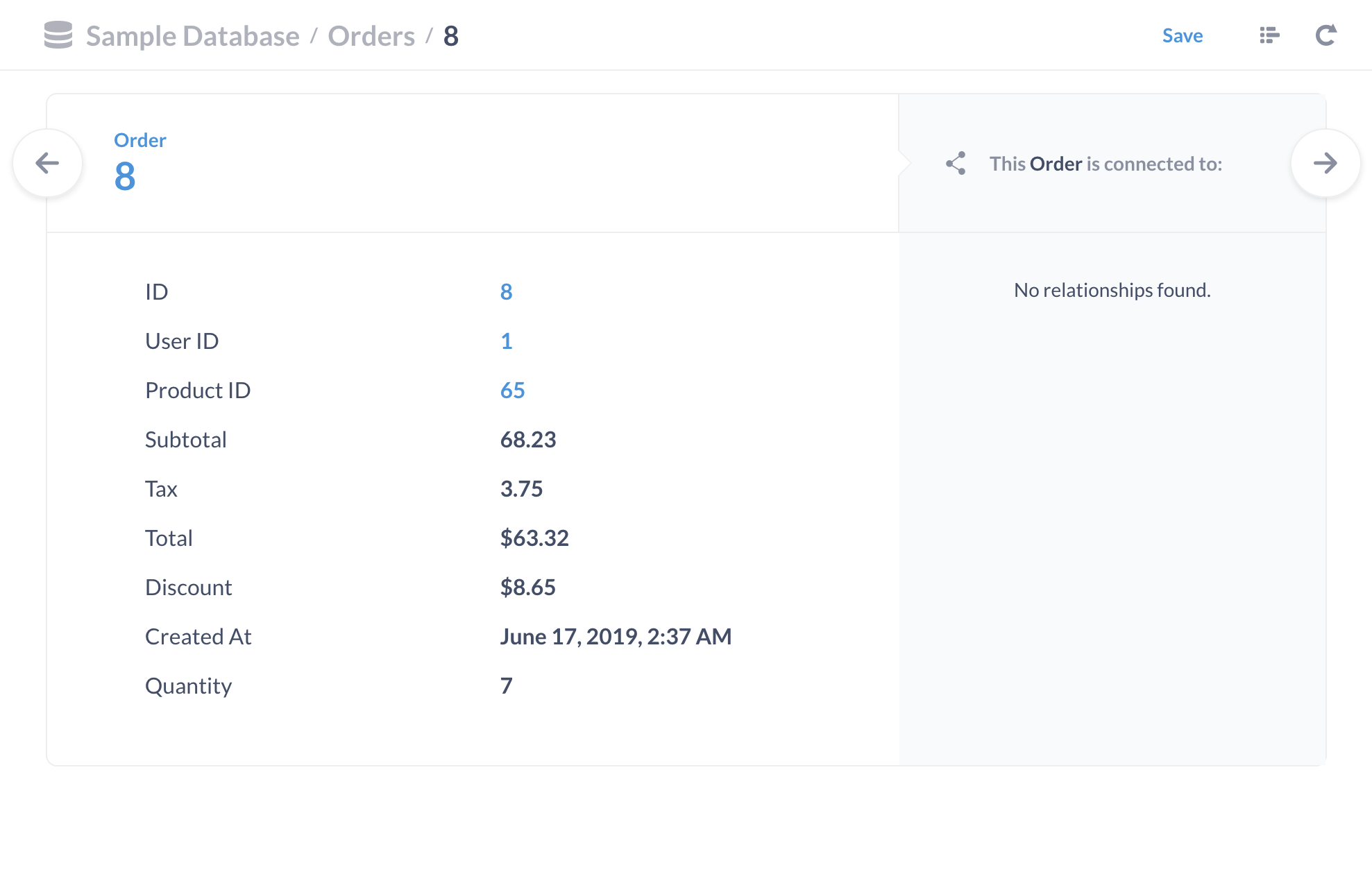
For example, we can see that the record (or row) with the ID of 8 was an order with a subtotal of $68.23, a discount of $8.65, and was created on June 17, 2019. The record right below it, with an ID of 9, follows the same structure, even though its values differ.
We can click on the ID field to get a better view of a record itself, like in figure 2: