What is an attribute?
An attribute is a property that describes or identifies some entity.
People in the data world use “attribute” in a few different contexts, so we’ll do our best to disambiguate here. Basically, an attribute is a characteristic of something. That something might be a table, but attribute could also refer to a characteristic of a specific record, like user attributes in Metabase.
Attributes in relational databases
In relational databases, people often use attribute synonymously with column or field, like how a product’s Category is an attribute of (or describes) that product. This usage of attribute comes up a lot within the context of data modeling and when designing entity relationship diagrams.
Example attribute
Here’s a look at the People table in Metabase’s Sample Database, which includes fields like ID, Name, Address, City, State, and so on:
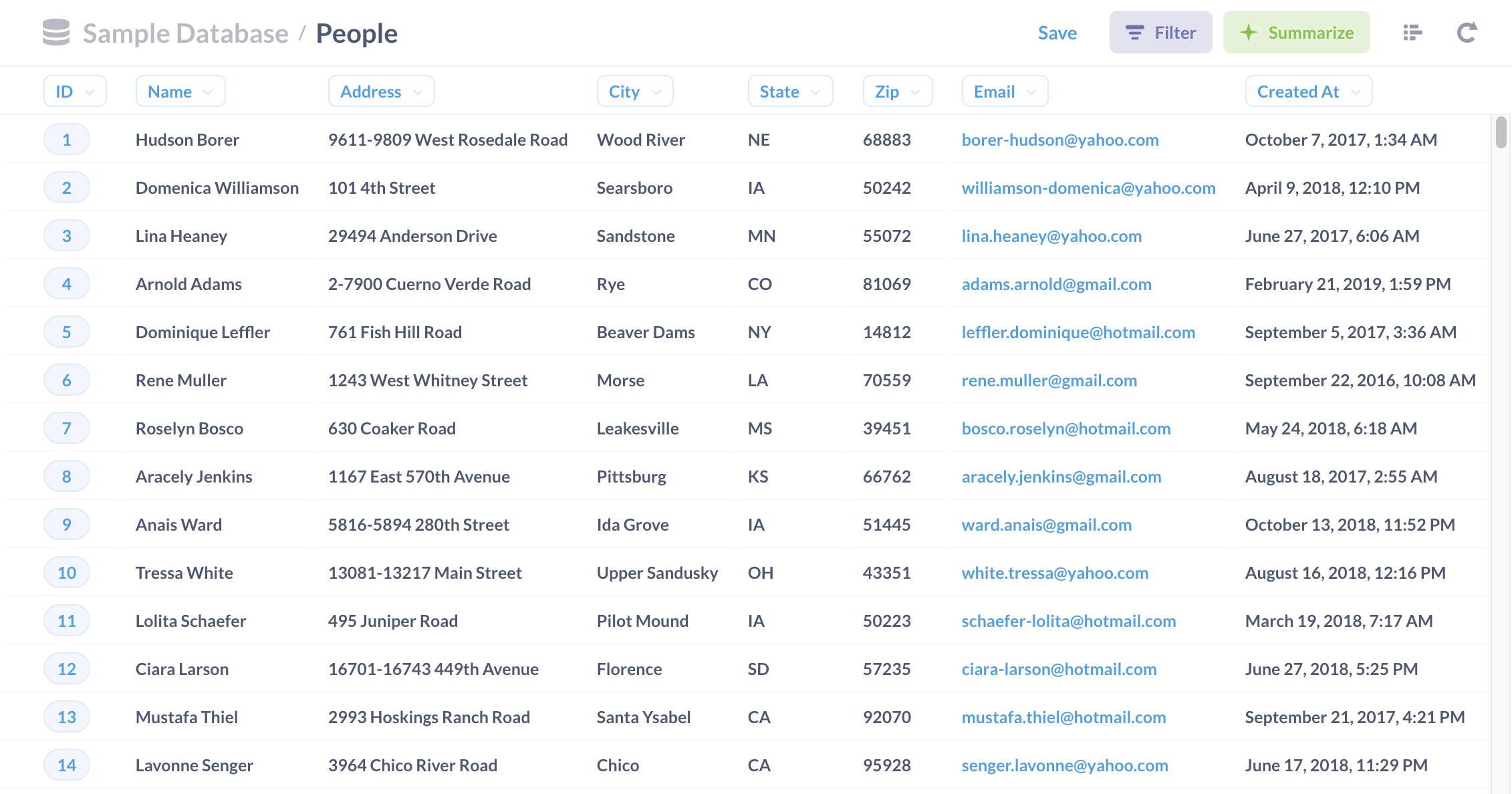
Each of these fields is an attribute — the values in those fields describe something about the record they’re associated with, in this case a “person” in the People table.
User attributes in Metabase
Sync user attributes is only available on Pro and Enterprise plans (both self-hosted and on Metabase Cloud).
Attribute can also refer to a distinct variable value that gets associated with a certain user, like a User_ID. That structure is known as a key-value pair, sometimes referred to as an attribute-value pair.
In Metabase, some plans allow you to set user attributes yourself (or pass them to Metabase via SSO). You can use these user attributes to set up custom destinations on a dashboard, for example by using a user ID to parameterize a URL when that user clicks on a chart.
User attributes are also an important part of data sandboxes, which give you granular control over the data that people using your Metabase instance can access. Since data sandboxes are associated with individual users, setting distinct user attributes lets Metabase know exactly how to filter a table depending on who views it.
Related terms
Further reading
- Authenticating with Google Sign-In or LDAP
- Data sandboxing: setting row-level permissions
- Advanced data sandboxing: limiting access to columns